(CNN Spain) — According to information According to the World Health Organization (WHO), obesity has tripled since 1975. The most recent data, from 2016, shows that more than 1.9 billion adults in the world are overweight, of whom around 650 million are obese.
Obesity and overweight are currently of epidemic proportions, it states The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), which adds that it is a major risk factor for a range of chronic diseases “including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and cerebrovascular accidents, as well as various types of cancer”.
This data poses an enormous global challenge in dealing with disease which, however, is often approached inappropriately. According to WHO, obesity can be prevented.
Here, everything you need to know about obesity, its variants, and what causes them.
What do we talk about when we talk about obesity?
Obesity consists of abnormal or excessive accumulation of fat in the body which may be detrimental to health, according to the globally accepted definition.
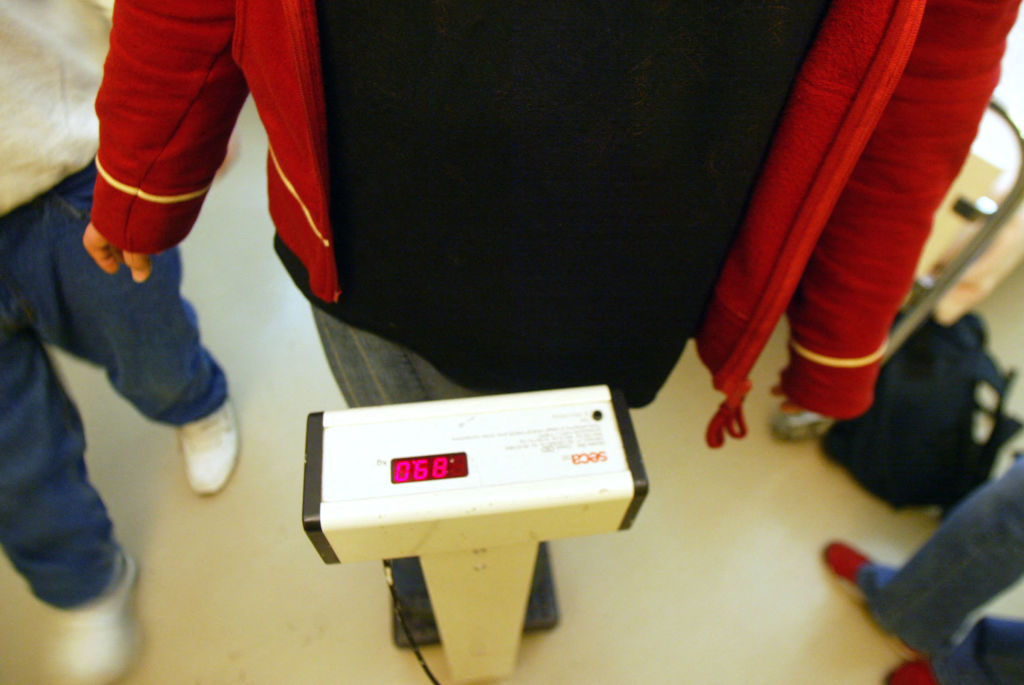
WHO uses technical definitions for obesity and overweight which are based on body mass index (BMI). It is an indicator that relates a person’s weight and height and is used to identify overweight and obesity in adults.
BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters (kg/m2). Thus, adults are considered overweight if their BMI is between 25 and up to 30, and they are considered obese if their BMI is equal to or greater than 30.
The National Health Service of the United Kingdom (NHS, in English) recognizes that the BMI indicator is useful for determining whether a person is at a healthy weight, warned which has some limitations because it measures a person’s weight, but does not differentiate between fat and muscle.
“People who are very muscular, such as professional athletes, can have a high BMI without too much fat,” he says.
What is morbid obesity?
Among cases of obesity, the The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines that there are different categories, according to the patient’s BMI index.
Someone in front of the scales.
Grade 1 obesity has a BMI between 30 and 35, grade 2 obesity has between 35 and 40, and grade 3 obesity has a BMI over 40. The latter is considered severe obesity, also known as “morbid obesity.” .
What caused it?
According to WHO, the cause of obesity and overweight is “an energy imbalance between calories consumed and calories expended”. According to the organization, there are two factors behind the growth of the disease: an increase in high-calorie, high-fat diets, coupled with the spread of a sedentary lifestyle.
While useful as an overview, an increasing number of definitions analyze multi-causal scenarios to explain the “epidemic” of overweight and obesity.
That The CDC refers to obesity and overweight as a “complex” disease, stating: “Many factors can lead to excessive weight gain, including diet, level of physical activity, and sleep routines. Social determinants of health, genetics, and food intake, certain medications also play a role.” “
In this context, beyond individual recommendations aimed at reversing the energy imbalances referred to by WHO, specific organizational lines of action are increasingly aimed at attacking the structural causes of this disease.
PAHO refers to a policy of action aimed at structural changes such as improving primary care and promoting healthy breastfeeding and care; improve nutrition and increase physical activity in educational settings; and policies that among others are aimed at regulating food marketing and labeling.

“Internet trailblazer. Troublemaker. Passionate alcohol lover. Beer advocate. Zombie ninja.”