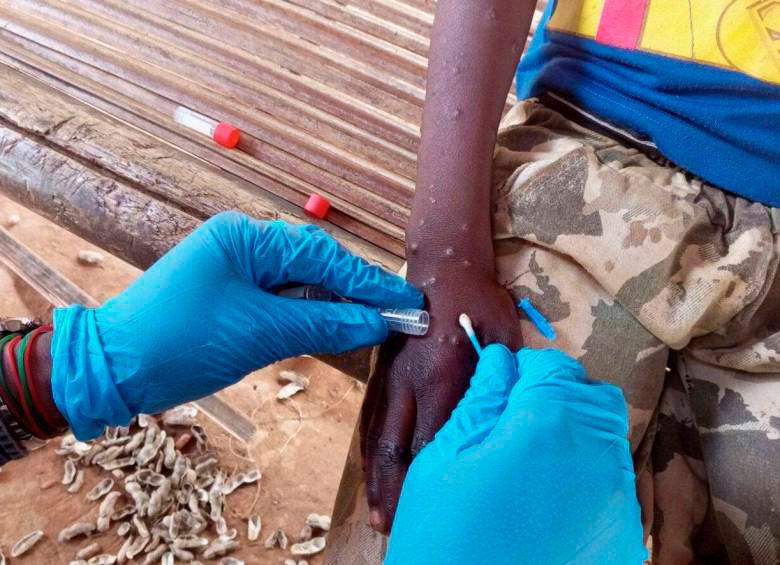
That Public Health Commission will try this thursday response documents and previous actions bird flu, documents covering, among other things, systems dual surveillance for anyone exposed on the farm to infected birds and minkseven with Individual Protection Equipment (EPI), as well as screening to improve detection of asymptomatic patients.
This is stated in the plan prepared by Alert Presentation and Preparedness and Response Plan and it updated action guidance for the Coordinating Center for Health and Emergency Alerts (CCAES) after confirming new cases last year in the State and Europe.
Although the possibility of bird flu transmission to humans is rareeven in contact with sick animals, Health is working to strengthen action and prevention protocols because “future cases” are not ruled out.
risk
Among the risks, the document cites, are Avian viruses evolve and increase their transmission capacity in humans because “it can happen through acquisitions mutation that provide adaptation of avian to mammalian viruses or through exchange or rearrangement of viral genome segments between different influenza viruses that infect different species and coincide in the same individual, animal or person”.
Thus, Health is forced to provide Public Health –within 72 hours of being notified of the outbreak – a list of persons exposed and who will be subject to “double surveillance” which allows suspicious cases to be detected as early as possible” and “increases the likelihood of detecting asymptomatic cases”, by passive surveillance of compatible symptoms or PCR screening.
“Due to the high volume of aerosols that can be generated in this outbreak and in the cleaning and disinfection tasks stemming from it, people associated with the focus (including agricultural workers and people engaged in control tasks) will be considered exposed regardless of the use of PPE during the exhibition”, explains the document.
Last year background
That September 27, first infection confirmed in a young worker from one Guadalajara Ranchasymptomatic and with a low viral load, and concluded that these findings relate to “contamination of the surface of the nasal or pharyngeal membranes”, although this could not be specifically demonstrated.
The worker is isolated until the next day, a negative PCR is performed, and a close contact study is also performed which is also negative.
Since January 2022, when the first positive was detected in the UKIn the State, controls were performed on workers from 22 farms and, out of 177 tests performed on 253 exposed employees, all but the cases mentioned above were negative.
So far, the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (MAPA) has notified the total 85 spotlights A(H5N1) in wild fowl -31 of them in summer- in 31 provinces and 36 outbreaks in poultry farms in 6 provinces.
possible future cases
The document states that the application of mEarly detection measures may lead to “more sporadic cases in the future” notificationso it’s obvious that this is very important “maintain and strengthen” surveillance in agriculture and prevention and control measures in at-risk groups (farmers, veterinarians, farm workers, hunters, ornithologists, environmental agents, zoo staff, etc.).
It demonstrates that avian influenza is a viral disease with worldwide distribution, maintained primarily among wild waterbirds and recalls that, until recently, “most of the influenza A virus subtypes that cause avian influenza have been relatively harmless to humans.” their natural bird hosts and do not usually infect humans.

“Internet trailblazer. Troublemaker. Passionate alcohol lover. Beer advocate. Zombie ninja.”